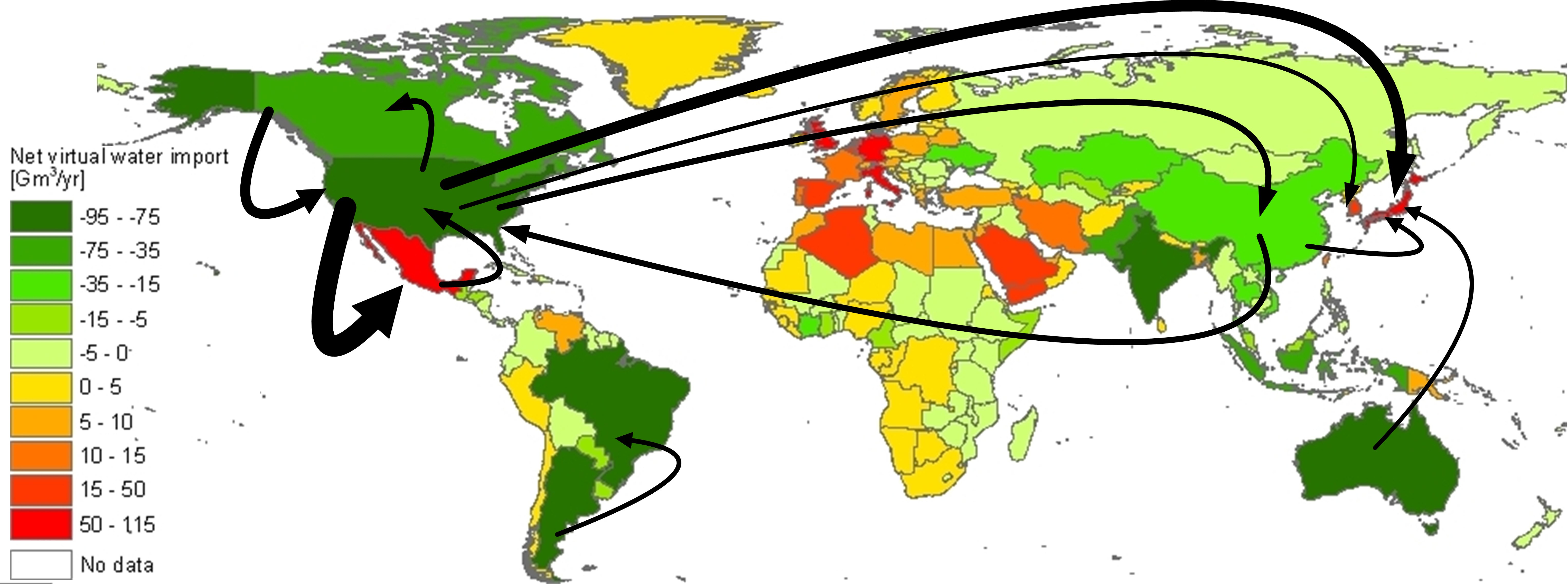
The U.S. is 20% dependent on “virtual” water, a large part of it from China, according to a new study from the University of Twente in the Netherlands.
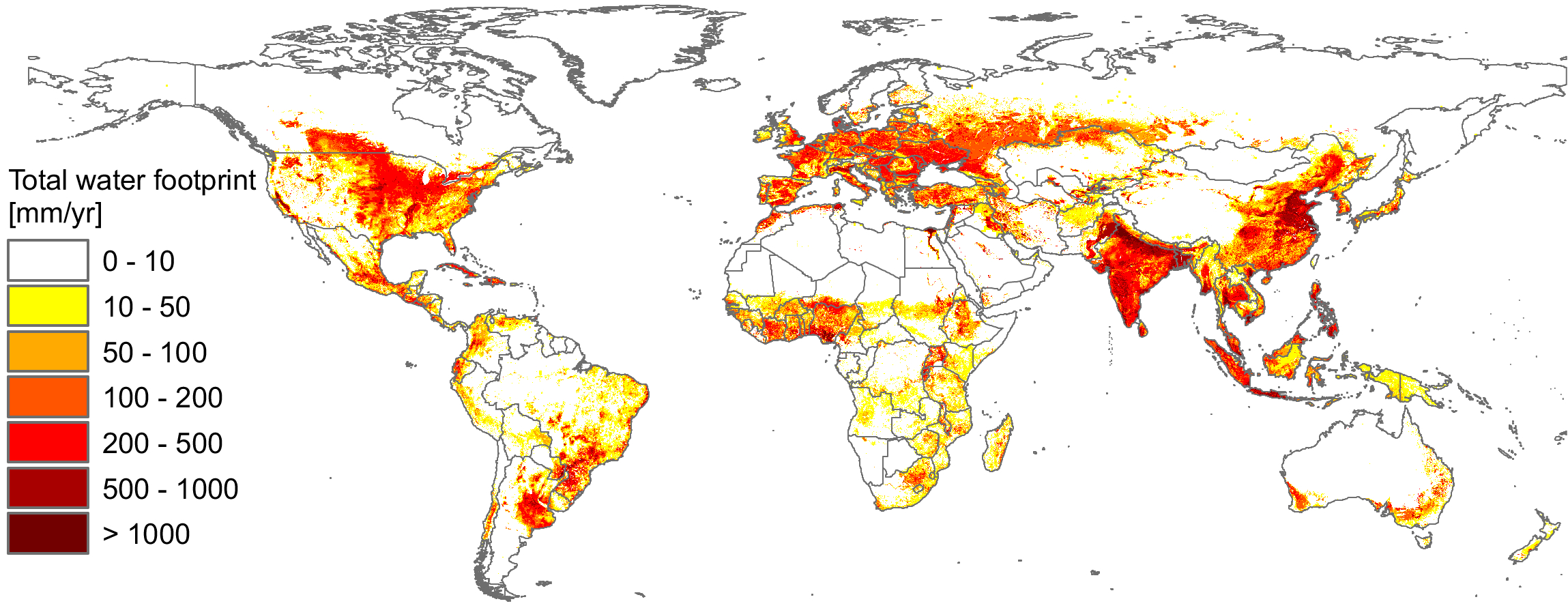
“The Water Footprint of Humanity” (PDF) examines global water-use patterns from 1996 to 2005 and calculates countries’ overall and per capita footprints based on the volume of rainwater consumed, groundwater and surface water depleted, and fresh water polluted. Humanity’s water footprint is estimated at 9,087 Gm3/yr, with 92% used in agriculture.
With 5% of the world’s population, the U.S. is the third-largest consumer of fresh water; per capita, U.S. citizens have a water footprint of 2,842 m3/yr—more than double the global average footprint of 1,385 m3/yr (partly because Americans’ beef consumption is 4.5 times the global average). When a crop is grown for export, water used in its production is “virtually” consumed by the importing country.
Virtual water, one-fifth of global water consumption, is largely related to oil crops (particularly cotton) and cereals, and flows highlight countries’ depletion and pollution of water beyond their borders; these “externalized footprints” are important in considering national food security.
For more information, see www.waterfootprint.org.
Add new comment
To post a comment, you need to register for a BuildingGreen Basic membership (free) or login to your existing profile.